Cattle

Cattle for Sale in Australia - Livestock Marketplace
Australia's cattle industry represents the backbone of our agricultural economy, contributing over $11 billion annually to national GDP whilst supporting thousands of regional communities across the continent.
The sector's sophistication has evolved considerably, with modern livestock trading now encompassing diverse purchasing methods, extensive breed selections, and advanced breeding technologies that cater to operations ranging from boutique farms to expansive pastoral stations.
Farmbuy Livestock stands at the forefront of this digital transformation, providing a comprehensive marketplace that connects buyers with reputable breeders and quality cattle across all states and territories. Whether you're starting a herd, expanding operations, or improving genetics, understanding how to buy cattle from auctions to embryo programs is key to making informed decisions that meet both short-term and long-term goals.

Cattle Studs
Cattle Livestock Listings













Latest Cattle News

Glendan Park's 13th annual bull sale at Barfold on Friday saw a major lift in the average price and clearance rate.

The Gommers family set an equal stud record price for an Angus bull at their Mandayen sale at Keith on Wednesday, attracting attention from...

Bulls with carcase traits and cutting-edge genetics were in demand at the 27th annual Yavenvale Poll Herefords sale at Adelong on February...

Many eyes in the Angus breed were on Nampara Eyes On You V61 ahead of the Hann family's annual bull sale at Lucindale so it was no surprise...

A single sire can influence hundreds of progeny throughout your breeding programme.

Bovine Ephemeral Fever, more commonly known as three-day sickness, can devastate herds, cripple productivity and erode profits, but there...

Bovine Respiratory Disease (BRD) has become the most common health problem in feedlot cattle and poses significant threats during this...

Another successful combined agents weaner sale at Boyanup last week had vendors and agents smiling alike, with one vendor saying a pen of...

Bulk buyers from Sarina bought the top bull at the 2025 Kandanga Valley Stud summer bull sale, where the sale average and clearance were up...

The cattle quality made the judging difficult at the ninth annual Elders Great Southern All Breeds Feeder and Weaner Show Sale at the Mount...

A total of just more than 1100 weaners were penned at the Elders and Nutrien Livestock combined weaned weaner sale at Boyanup , with strong...

A younger and slightly lighter yarding of cattle filled the Boyanup saleyards last Friday, when the Elders South West team yarded just...
Cattle Purchase Methods in Australia
Auction Sales
The traditional livestock auction remains a cornerstone of Australian cattle trading, offering transparent price discovery through competitive bidding whilst providing buyers the opportunity to assess multiple lots in a single venue. Modern auctions blend traditional physical saleyard practices with digital platforms, enabling remote participation and expanding market reach beyond geographical constraints. Registered bidders gain access to comprehensive vendor declarations, health certificates, and breeding records, which facilitate informed purchasing decisions.
Buy Now Options
Direct purchase arrangements through fixed-price listings offer certainty and efficiency for buyers who require immediate stock acquisition, eliminating the variables of auction competition. This method particularly suits time-sensitive restocking needs, allowing purchasers to secure specific cattle that meet predetermined criteria whilst negotiating delivery timeframes and payment terms directly with vendors, streamlining the transaction process for both parties.
Classified Listings
Private seller marketplaces provide detailed specifications about individual animals or lots, including comprehensive breeding histories, performance data, and genetic profiles, which enable buyers to make informed targeted selections. These listings facilitate direct communication between buyers and sellers, fostering relationship building while allowing for negotiation on price, delivery arrangements, and potential viewing opportunities before a commitment is made.
Paddock Sales
On-farm inspections provide invaluable insights into cattle temperament, condition, and adaptation to local environments, allowing buyers to observe stock in their natural settings whilst assessing farm management practices and breeding programme quality. These sales often yield long-term supplier relationships, with buyers gaining confidence through direct interaction with breeders who possess intimate knowledge of their cattle's lineage, health history, and performance characteristics.
Dispersal Sales
Complete or partial herd dispersals present unique opportunities to acquire proven genetics from established breeding programmes, often including elite bloodlines that would otherwise remain unavailable. These sales, typically triggered by retirement, property sales, or strategic business restructuring, offer buyers access to decades of selective breeding work. Lots frequently include detailed performance records, progeny data, and an established reputation within breed societies.
Cattle Availability Across Australian States and Territories
Major Cattle Regions
- Queensland dominates national beef production with over 11 million head, specialising in tropical breeds adapted to northern Australia's challenging climate.
- New South Wales combines extensive pastoral operations with intensive feeding systems across diverse geographical zones from coastal regions to western plains.
- Victoria excels in both dairy and premium beef production, leveraging temperate conditions and reliable rainfall to support year-round pasture systems.
- Western Australia, on the other hand, focuses on export-quality cattle suited for live shipping and processing for international markets. South Australia emphasises sustainable farming practices and premium grass-fed production.
- Tasmania capitalises on its disease-free status and pristine environment for boutique operations.
- The Northern Territory manages vast stations that require hardy, low-maintenance breeds.
- The Australian Capital Territory supports small-scale, quality breeding programmes serving local and regional markets.
Regional Considerations
Interstate cattle movement requires careful consideration of biosecurity protocols, including health certification, compliance with the National Livestock Identification System, and potential quarantine requirements that vary between jurisdictions.
Climate adaptation significantly influences breed selection, with tropical breeds essential for northern regions, whilst temperate breeds thrive in southern states.
Transportation logistics must account for distance, animal welfare requirements, and seasonal conditions that affect road access to remote properties, all while navigating regional price variations influenced by local supply-demand dynamics, processing facility proximity, and export market access.
Cattle Breed Guide
British and European Breeds
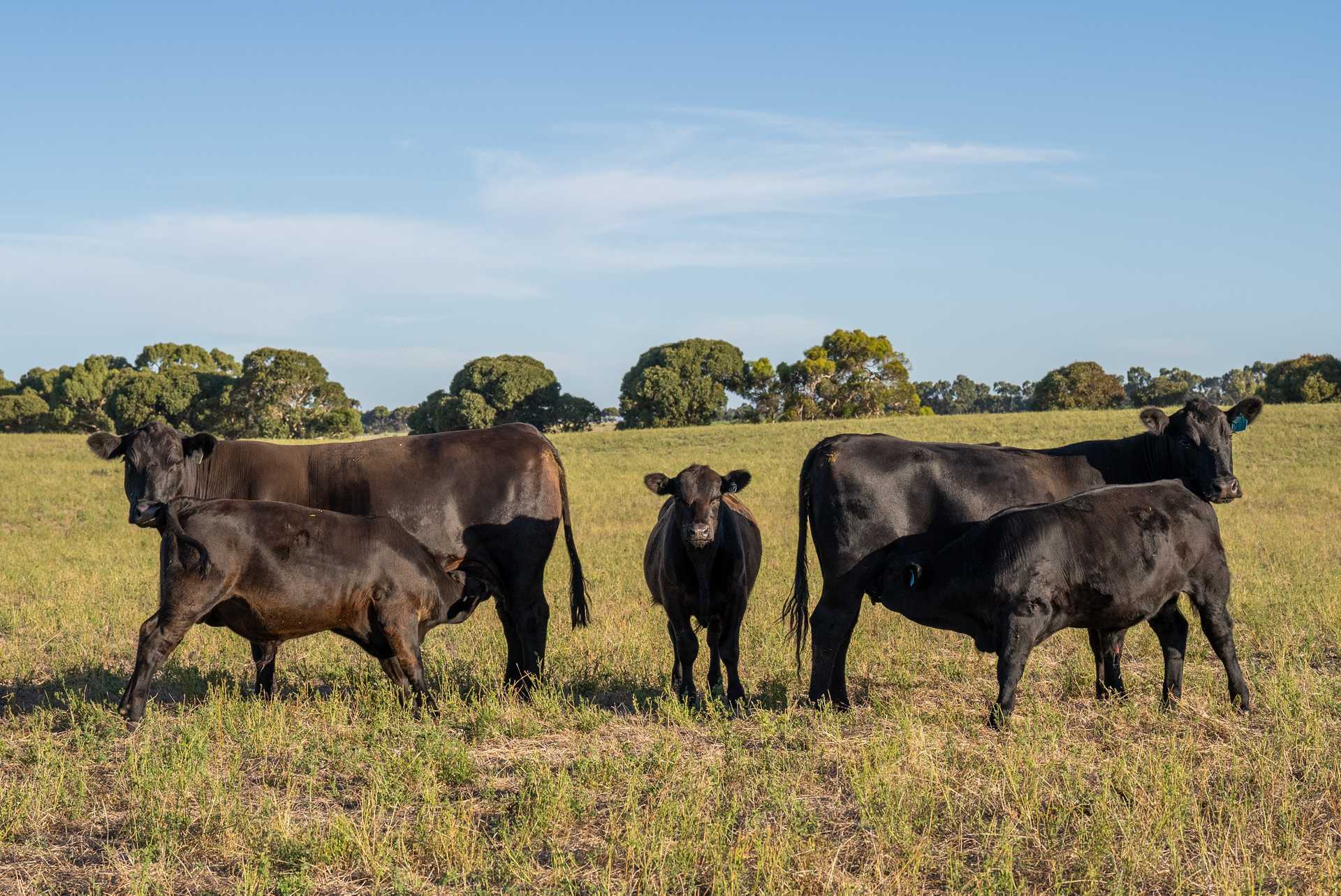

Angus cattle
Dominate premium beef markets with exceptional marbling, early maturity, and consistent carcass quality.
Charolais
Deliver superior growth rates and lean meat yields, favoured by processors for efficiency.
Black Simmental
Combine the traditional Simmental's dual-purpose versatility with improved carcass traits.
Devon cattle
Preserve heritage genetics valuable for grass-finishing systems.
Dexter cattle
Ideal for small-scale operations thanks to their compact size and feed efficiency.
British White cattle
Support conservation programs while offering unique marketing opportunities.
Belted Galloway
Recognised for their distinctive appearance and hardy nature, suited to extensive grazing systems.
Brown Swiss
Excel in dairy production with high milk components and longevity, showcasing the diversity of European-origin breeds.
Continental European Breeds

Belgian Blue
Known for exceptional muscling and lean meat production, revolutionising beef efficiency standards but requiring careful management and calving assistance.
Blonde d'Aquitaine
Showcases French breeding excellence with strong feed conversion efficiency and high carcass yield.
Chianina
The world's largest cattle breed, valued for its impressive frame size and growth potential for specialised markets.
Fleckvieh
A true dual-purpose breed, balancing high milk production with strong beef characteristics.
Braunvieh
Originating from the Alps, highly adaptable to varied Australian conditions while maintaining excellent production efficiency.
Tropical and Composite Breeds
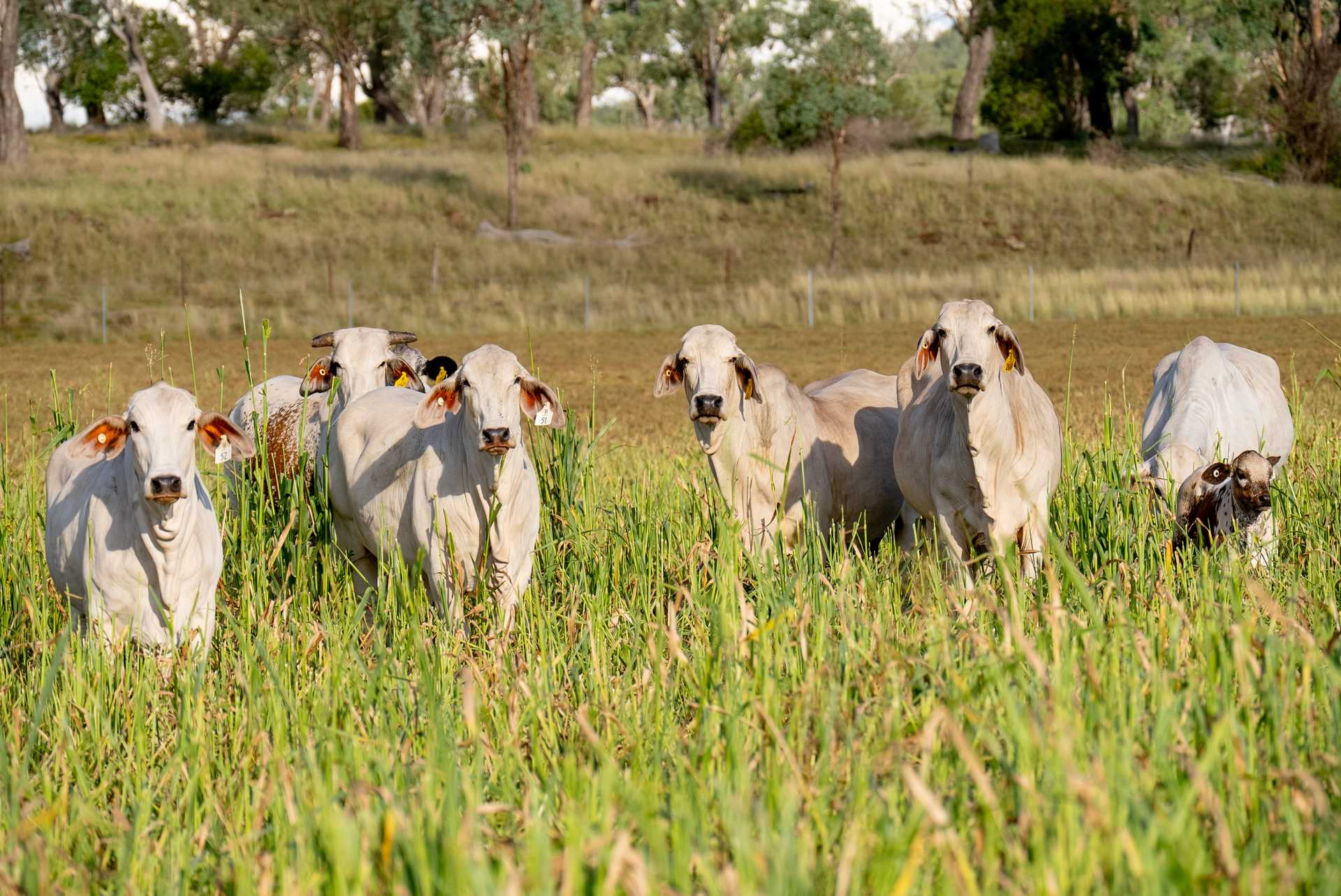

Brahman
Renowned for heat tolerance and parasite resistance, forming the foundation of northern Australian beef production. Their genetics underpin composite breeds like
Droughtmaster
Developed for Queensland conditions by combining Brahman hardiness with British beef quality.
Beefmaster
A three-breed hybrid designed for commercial efficiency and strong hybrid vigour.
Brangus
Combines Angus meat quality with Brahman adaptability to tropical environments.
Braford
Merges Hereford traits with Brahman resilience for reliable tropical performance.
Charbray
Integrates Charolais growth and muscling within a heat-tolerant framework.
Bonsmara
A South African breed offering proven tropical genetics suited to Australian conditions.
Drakensberger
Another South African breed valued for adaptability, fertility, and carcass quality in warm climates.
Belmont Red
An Australian-developed composite showcasing innovation in breeding for tropical efficiency and productivity.
Cattle Categories and Breeding Options
Traditional Livestock Categories
Bull selection remains fundamental to genetic improvement, requiring assessment of structural soundness, breeding soundness examination results, and estimated breeding values that predict progeny performance across economically essential traits.
Proven cows offer immediate breeding capacity with established production records, whilst heifers represent future breeding potential requiring careful selection based on pedigree, phenotype, and genetic testing results. Steers provide straightforward finishing options for feedlot or grass-finishing systems, without breeding complexities. Calves offer growth potential for backgrounding operations, and cow-calf units deliver complete breeding packages, enabling immediate production while maintaining genetic continuity.
Advanced Breeding Technologies
Embryo transfer technology exponentially multiplies elite genetics, allowing single donors to produce multiple offspring annually while preserving valuable bloodlines and accelerating genetic gain through intensive selection.
Semen sales democratise access to superior sires, regardless of geographical location. Straws enable long-term storage and strategic deployment, aligning with breeding objectives. Meanwhile, flush programmes maximise donor potential through superovulation protocols, yielding multiple embryos per cycle for transfer or freezing.
Selection Considerations
Comprehensive health testing, including disease screening, fertility assessment, and genetic condition status, ensures biosecurity compliance while minimising production risks. Registration documentation and pedigree verification are critical for maintaining breed integrity and accessing premium markets.
Age considerations influence immediate productivity versus long-term potential.
Breeding history provides performance indicators, and a structural assessment remains fundamental, regardless of the intended use. Farmbuy facilitates access to verified health and registration information across all categories.
The Australian cattle marketplace offers unprecedented diversity in purchasing options, breed selection, and breeding technologies that cater to every production system and business objective.
From traditional auction rings to advanced reproductive technologies, today's cattle buyers benefit from transparent information, comprehensive health protocols, and nationwide accessibility that Farmbuy seamlessly facilitates through its integrated platform.
Success in cattle acquisition requires matching specific breed characteristics with environmental conditions, aligning purchasing methods with operational requirements, and leveraging available technologies to maximise genetic potential whilst maintaining biosecurity standards.
Whether sourcing tropical composites for northern stations or premium temperate breeds for intensive systems, informed decision-making supported by comprehensive market access ensures optimal outcomes for Australian cattle producers navigating an increasingly sophisticated livestock sector.
Frequently Asked Cattle Questions
What is the best cattle breed for beginners in Australia?
Angus and Hereford cattle provide ideal starting points due to their docile temperaments, broad environmental adaptability, and consistent market demand. They require less specialised management than tropical breeds, while offering reliable performance across varied production systems and strong resale values.
How much does it cost to buy cattle?
Current market conditions indicate that weaner prices range from $800 to $1,500 per head, depending on weight, breed, and quality. Meanwhile, quality breeding stock commands $2,500-$5,000 for commercial females and $3,000-$10,000 for registered bulls, with elite genetics potentially exceeding these ranges significantly.
Do I need a licence to buy cattle in Australia?
Do I need a licence to buy cattle in Australia? Property Identification Codes remain mandatory for keeping livestock, with National Livestock Identification System registration required for all cattle movements. Specific state regulations may impose additional requirements for commercial operations or interstate trading.
What's the difference between auction and paddock sales?
Auctions provide competitive price discovery and multiple purchasing options within a single venue, while paddock sales enable thorough on-farm assessment, direct breeder relationships, and negotiation flexibility. Each method suits different buyer preferences and operational requirements.
Which Australian state has the best cattle?
Each state's specialisation reflects environmental advantages: Queensland excels with tropical breeds, Victoria dominates dairy production, New South Wales offers diversity, Western Australia focuses on export quality, with selection depending on specific operational requirements rather than absolute superiority.
How do I transport cattle across state lines?
Interstate movement requires health certificates from accredited veterinarians, completion of NLIS transfer, potential quarantine periods depending on disease status, and the engagement of licensed transporters familiar with route requirements, rest stop regulations, and destination facility specifications.
What are composite cattle breeds?
Composite breeds strategically combine multiple breed genetics to optimise specific traits, such as heat tolerance, growth rates, and meat quality. Examples include the Droughtmaster, Beefmaker, and Belmont Red, which were developed specifically for Australian conditions.
Is buying embryos or semen worth it?
Embryo transfer and artificial insemination offer cost-effective access to elite genetics, eliminating the need to purchase expensive sires. However, they require technical expertise, specialised facilities, and synchronisation programmes that increase management complexity compared to natural breeding.
What are maternal flush sheep and why are they valuable?
Maternal flush programmes involve superovulating elite ewes to produce multiple embryos for transfer, rapidly multiplying superior genetics and accelerating genetic gain in both stud and commercial operations.
What should I check before buying cattle?
Essential verification includes current health status, vaccination history, NLIS compliance, vendor declarations, structural soundness, breeding records, and biosecurity certificates, with personal inspection or trusted agent assessment recommended before finalising purchases.
When is the best time to buy cattle in Australia?
Autumn offers quality weaners following summer growth, while spring provides breeding stock before joining. Market conditions, seasonal forecasts, and feed availability should guide timing decisions more than calendar dates alone.
How many cattle do I need to start a farming operation?
Viable numbers depend on property carrying capacity, infrastructure, and business objectives. Small properties typically support 10-20 head for supplementary income, while commercial viability requires a minimum of 50-100 head, depending on the production system and market access.